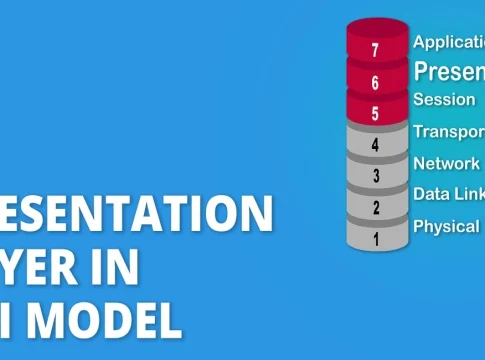
The presentation layer is the sixth layer in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, a conceptual framework for networking. This layer acts as a translator, mediating between the application layer, which deals with user-specific protocols, and the lower network layers that handle data transmission.
Core Responsibilities
The primary function of the presentation layer is to ensure seamless data exchange between different systems by taking care of data presentation and interpretation. It achieves this by performing several key tasks:
- Data Formatting: The presentation layer translates data formats used by applications on one system into a format understood by applications on another system. This can involve converting character sets like EBCDIC (used by IBM mainframes) to ASCII (commonly used by personal computers), or adapting image or video data for compatibility across different operating systems or software versions. For instance, the presentation layer might convert a high-resolution image into a smaller, more web-friendly format for faster transmission.
- Data Encryption and Decryption: This layer plays a crucial role in data security by encrypting application data at the sending system and decrypting it at the receiving system. This ensures that only authorized parties with the appropriate decryption key can access the information. Encryption algorithms scramble the data using mathematical transformations, making it unreadable without the key. Common encryption standards like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are employed by the presentation layer to secure data transmission over networks like the internet.
- Data Compression and Decompression: The presentation layer can compress data before transmission to reduce network bandwidth usage and improve transmission speed. Large files, such as images and videos, can be significantly reduced in size by employing compression techniques. Upon reaching the destination, the data is decompressed for use by the application layer. Common compression schemes like GIF and JPEG are employed for images, while ZIP and RAR are popular for general file compression. The choice of compression method depends on the type of data and the desired balance between compression ratio and processing speed.
Benefits of the Presentation Layer
The presentation layer offers several advantages in network communication:
- Interoperability: By handling data format conversions, the presentation layer enables applications on different systems to exchange data seamlessly, regardless of their underlying architectures. This allows users on Windows PCs to collaborate with colleagues using Macs or Linux machines by ensuring their applications can understand each other’s data formats.
- Security: Encryption capabilities safeguard sensitive data during transmission, preventing unauthorized access. Financial transactions, medical records, and other confidential information can be protected from eavesdropping by encrypting the data at the presentation layer.
- Efficiency: Data compression techniques can significantly reduce the size of data packets, optimizing network bandwidth usage and transmission times. This is particularly beneficial for transmitting large files over limited bandwidth connections, such as dial-up internet or satellite communication.
Beyond the Basics
The presentation layer also facilitates tasks like:
- Multimedia Configuration: It can manage the format and encoding of multimedia data, ensuring proper display of images, audio, and video. The presentation layer might negotiate the appropriate codecs (compression/decompression algorithms) between sender and receiver to ensure smooth playback of multimedia content.
- Content Transformation: The layer can manipulate message content, such as character encoding or data structure, to suit the receiving system’s requirements. This can involve tasks like removing unnecessary control characters or adjusting data field lengths for compatibility.
- External Data Representation (XDR): The presentation layer utilizes XDR, a standard for exchanging data across heterogeneous systems. XDR converts local data representations into a universal format independent of the host system’s architecture. This ensures that the data structure and meaning are preserved during transmission, even between systems with vastly different internal representations.
In conclusion, the presentation layer acts as a bridge between the application layer and the lower network layers. It ensures that data is presented in a format that can be understood and processed by applications on different systems, promoting secure, efficient, and interoperable communication across networks. By handling data formatting, encryption, compression, and other tasks, the presentation layer plays a vital role in ensuring seamless and reliable data exchange in today’s complex networked world.
The presentation layer is the sixth layer in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, a conceptual framework for networking. This layer acts as a translator, mediating between the application layer, which deals with user-specific protocols, and the lower network layers that handle data transmission.
Core Responsibilities
The primary function of the presentation layer is to ensure seamless data exchange between different systems by taking care of data presentation and interpretation. It achieves this by performing several key tasks:
- Data Formatting: The presentation layer translates data formats used by applications on one system into a format understood by applications on another system. This can involve converting character sets like EBCDIC (used by IBM mainframes) to ASCII (commonly used by personal computers), or adapting image or video data for compatibility across different operating systems or software versions. For instance, the presentation layer might convert a high-resolution image into a smaller, more web-friendly format for faster transmission.
- Data Encryption and Decryption: This layer plays a crucial role in data security by encrypting application data at the sending system and decrypting it at the receiving system. This ensures that only authorized parties with the appropriate decryption key can access the information. Encryption algorithms scramble the data using mathematical transformations, making it unreadable without the key. Common encryption standards like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are employed by the presentation layer to secure data transmission over networks like the internet.
- Data Compression and Decompression: The presentation layer can compress data before transmission to reduce network bandwidth usage and improve transmission speed. Large files, such as images and videos, can be significantly reduced in size by employing compression techniques. Upon reaching the destination, the data is decompressed for use by the application layer. Common compression schemes like GIF and JPEG are employed for images, while ZIP and RAR are popular for general file compression. The choice of compression method depends on the type of data and the desired balance between compression ratio and processing speed.
Benefits of the Presentation Layer
The presentation layer offers several advantages in network communication:
- Interoperability: By handling data format conversions, the presentation layer enables applications on different systems to exchange data seamlessly, regardless of their underlying architectures. This allows users on Windows PCs to collaborate with colleagues using Macs or Linux machines by ensuring their applications can understand each other’s data formats.
- Security: Encryption capabilities safeguard sensitive data during transmission, preventing unauthorized access. Financial transactions, medical records, and other confidential information can be protected from eavesdropping by encrypting the data at the presentation layer.
- Efficiency: Data compression techniques can significantly reduce the size of data packets, optimizing network bandwidth usage and transmission times. This is particularly beneficial for transmitting large files over limited bandwidth connections, such as dial-up internet or satellite communication.
Beyond the Basics
The presentation layer also facilitates tasks like:
- Multimedia Configuration: It can manage the format and encoding of multimedia data, ensuring proper display of images, audio, and video. The presentation layer might negotiate the appropriate codecs (compression/decompression algorithms) between sender and receiver to ensure smooth playback of multimedia content.
- Content Transformation: The layer can manipulate message content, such as character encoding or data structure, to suit the receiving system’s requirements. This can involve tasks like removing unnecessary control characters or adjusting data field lengths for compatibility.
- External Data Representation (XDR): The presentation layer utilizes XDR, a standard for exchanging data across heterogeneous systems. XDR converts local data representations into a universal format independent of the host system’s architecture. This ensures that the data structure and meaning are preserved during transmission, even between systems with vastly different internal representations.
In conclusion, the presentation layer acts as a bridge between the application layer and the lower network layers. It ensures that data is presented in a format that can be understood and processed by applications on different systems, promoting secure, efficient, and interoperable communication across networks. By handling data formatting, encryption, compression, and other tasks, the presentation layer plays a vital role in ensuring seamless and reliable data exchange in today’s complex networked world.