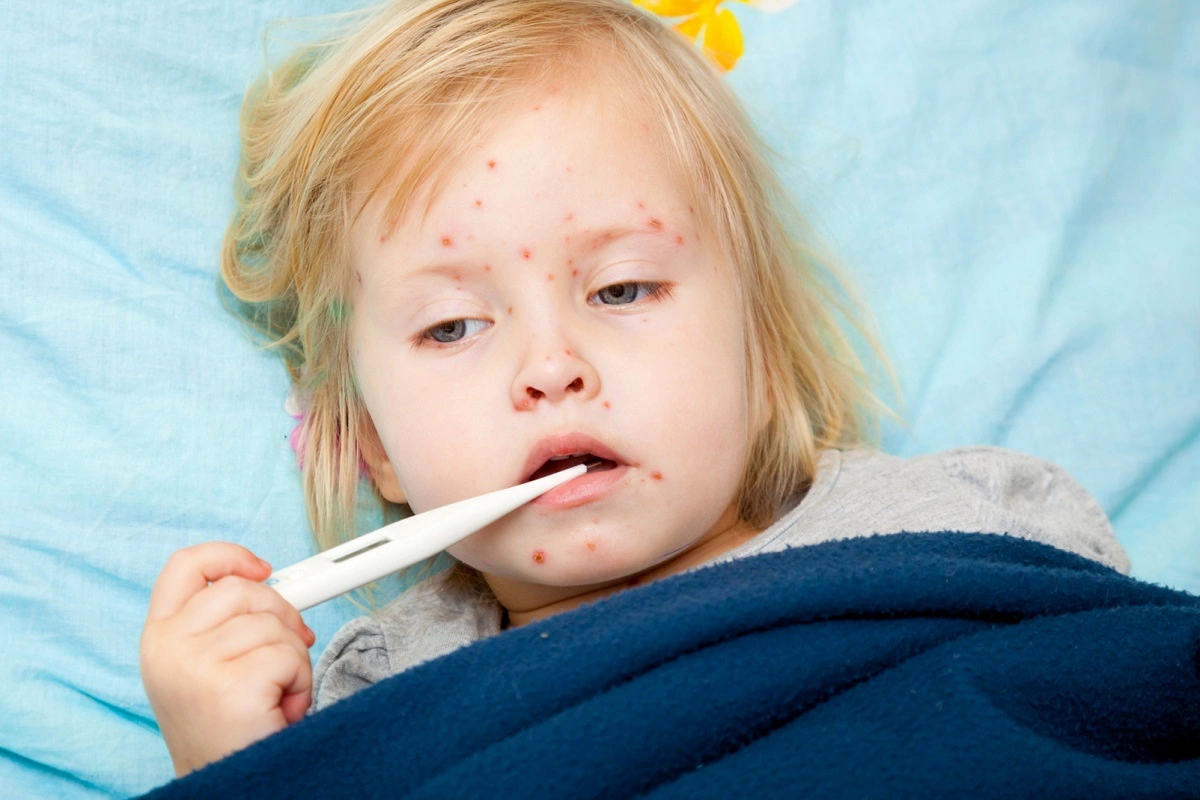
Measles is a disease that commonly affects children. It is described as a viral infection that is very contagious. Small white spots on the child’s body are the first symptom of measles. The spots, which are also referred to as Koplik’s spots, usually appear in the mouth of the child between 2 and four days after infection occurs. Other symptoms associated with measles include:
- Fever
- Runny nose
- Sore throat
- Hacking cough
- Red eyes
In some instances, the child becomes sensitive to bright lights.
Five days later the child gets a rash. While it is a mild rash it is very itchy. The first place that the rash appears is below and the front of the ears. As the disease progresses, the rashes may also appear on the sides of the neck, arms, legs and trunk. However, by this time it will have faded on the child’s face.
When the illness as its peak, the child will complain of feeling very weak and sickly. The rash will have spread to different parts of the body. What is more, the body temperature will have risen, and sometimes even exceeded 104 degree Fahrenheit. However, it is worth noting that some children develop what is referred to as encephalitis. This is a term used to refer to brain infection. A child that develops encephalitis because of measles experiences the following symptoms:
- High fever
- Seizures
- Coma
Measles increases a child’s susceptibility to bacterial infections. Accordingly, a child suffering from measles get pneumonia as well as infection in the middle ear. Measles may cause lowering in the levels of blood platelets in the child’s body. The consequence of this is that the child bleeds and bruises very easily. However, this happens in very rare cases. All these symptoms usually appear between 7 and 14 days after infection occurs.